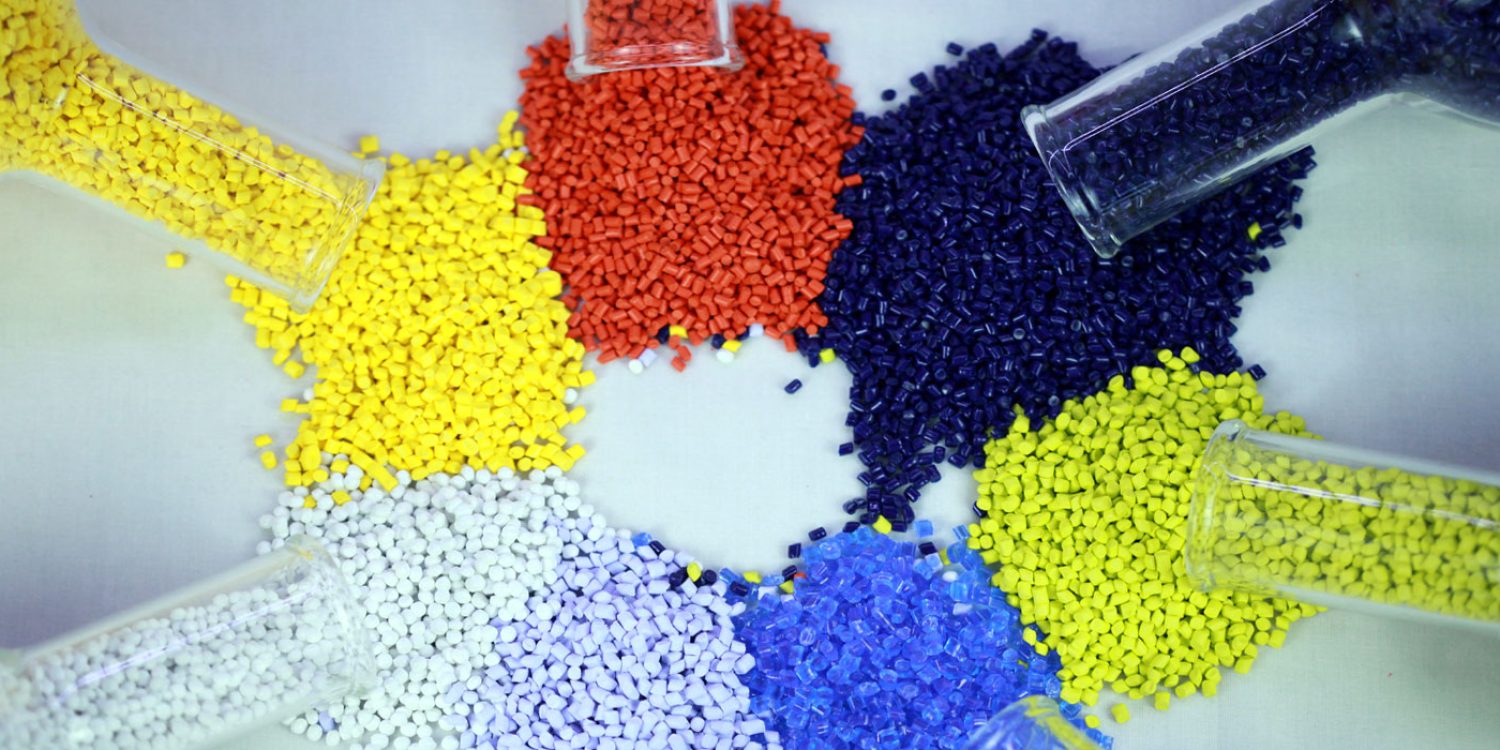
Masterbatches are concentrated mixtures of pigments, additives, or modifiers that are used to color or enhance the properties of plastics, rubber, or other materials during the manufacturing process. They are widely used in industries like packaging, automotive, construction, and more. There are several types of masterbatches based on their purpose and composition:
- Color Masterbatch: These are the most common type of masterbatches. They contain concentrated pigments and additives that provide color to the final plastic product. Color masterbatches help achieve consistent and uniform coloration throughout the material.
- Additive Masterbatch: These masterbatches contain additives that enhance the properties of the final product. They can include additives such as UV stabilizers, antioxidants, anti-static agents, flame retardants, slip agents, and more. Additive masterbatches allow manufacturers to incorporate specific properties into the plastic without needing to mix individual additives.
- White Masterbatch: White masterbatches are used to achieve opaque white coloration in plastics. They contain titanium dioxide as the primary pigment. White masterbatches are commonly used in applications where a solid white color is required, such as in packaging and consumer goods.
- Black Masterbatch: Similar to white masterbatches, black masterbatches are used to achieve deep black coloration in plastics. They usually contain carbon black as the main pigment. Black masterbatches are used for applications where a strong black color is desired.
- Filler Masterbatch: Filler masterbatches contain mineral fillers like calcium carbonate, talc, or clay. These fillers are added to the plastic material to reduce cost, improve mechanical properties, and enhance processing characteristics. They are often used in applications where cost-effectiveness and certain physical properties are important.
- Special Effect Masterbatch: These masterbatches provide unique visual effects, such as pearlescent, metallic, glitter, or marble-like appearances. They are used to give the final product a distinctive and visually appealing look.
- Polymer-specific Masterbatch: Some masterbatches are designed for use with specific types of polymers, such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), etc. These masterbatches are formulated to work optimally with the processing conditions and characteristics of the chosen polymer.
- High-Performance Masterbatch: These masterbatches are engineered to provide advanced properties such as high heat resistance, chemical resistance, improved mechanical strength, and more. They are used in demanding applications like automotive parts, electrical components, and industrial equipment.
- Foaming Masterbatch: Foaming masterbatches are used to introduce controlled voids or bubbles into plastics, reducing their density while maintaining mechanical properties. This can lead to cost savings and improved insulation properties in certain applications.